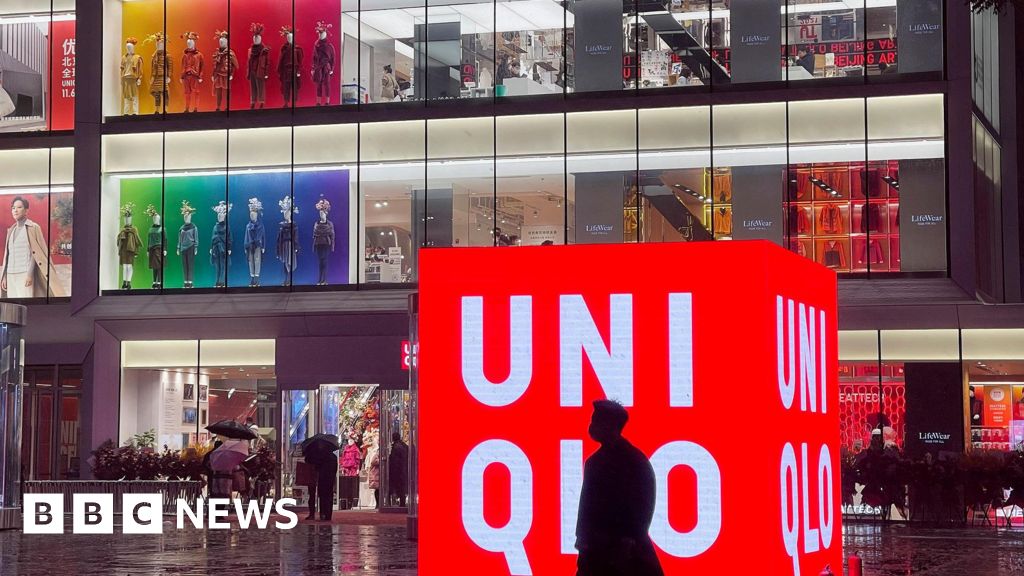
In 2022, tough US regulations on the import of goods from Xinjiang came into effect.
Many global brands removed products using Xinjiang cotton from their shelves, which led to fierce backlash in China. Brands such as H&M, Nike, Burberry, Esprit and Adidas were boycotted.
Sweden’s H&M saw its clothing pulled from major e-commerce stores in China.
At the time, Mr Yanai – who is Japan’s richest man – refused to confirm or deny whether Xinjiang cotton was used in Uniqlo clothing, saying he wanted “to be neutral between the US and China”, external.
His decision not to take a side helped Uniqlo to remain popular in China’s huge retail market.
But speaking to the BBC in Tokyo about the firm’s measures to be more transparent about where the materials in its clothes come from and how they are made, he said: “We’re not using [cotton from Xinjiang].”
“By mentioning which cotton we’re using…” he continued, before pausing and ending his answer with “Actually, it gets too political if I say anymore so let’s stop here”.
Isaac Stone Fish, the chief executive and founder of Strategy Risks, a business intelligence firm with a China focus highlights the pressures on firms from both China and the US.
“Not a single large company can remain politically neutral anymore,” he says.
“Both Beijing and Washington want companies to choose sides, and Tokyo will continue to lean closer to the United States in this matter.”
Even though Uniqlo has been expanding aggressively in Europe and the US, in Mr Yanai’s own words, “we are not a known brand globally” and Asia is still its biggest market.
The company has more stores in China than in its home country Japan, and Mr Yanai says he does not plan to change that strategy despite challenges in the world’s second biggest economy.
“There are 1.4 billion people in China and we only have 900 to 1,000 stores,” he says. “I think we can increase that to 3,000.”
Meanwhile, China is Uniqlo’s single biggest manufacturing hub. The company also makes clothes in countries including Vietnam, Bangladesh, Indonesia and India.
In 2009, when 80% of its products were made in China, external, Mr Yanai told the BBC that China was getting too expensive and the firm was shifting production away “to lower-wage Cambodia to keep prices low”.
He now says it was challenging to repeat China’s success as the world’s factory in other countries as transferring years of experience proved difficult.
Credit: Source link