There’s no debate that when it comes to succeeding in digital content, mastering SEO is a must. When I first became a content writer, most of the advice I received was about keywords, backlinks, relevancy, and improving user experience.
![Download Now: 100 ChatGPT Prompts for Marketers [Free Guide]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/c497a8fe-0f60-4244-9cb1-5bed4d1e5ab6.png)
However, as technology has advanced, SEO has changed. We’re entering a new era of search — the AI age — and, with it, a new type of digital content technique.
Enter: Generative Engine Optimization (GEO).
How we obtain information now has changed dramatically as a result of AI. More than ever, people rely on generative engines for information, making learning how to optimize for AI essential.
If we want our content to reach the right people, we need to adapt. There’s no need to throw out the SEO principles you’ve spent decades learning. GEO is an extension of these techniques — and it’s not as scary as it sounds.
Let’s take a look at what we know about GEO so far.
Table of Contents
What is Generative Engine Optimization?
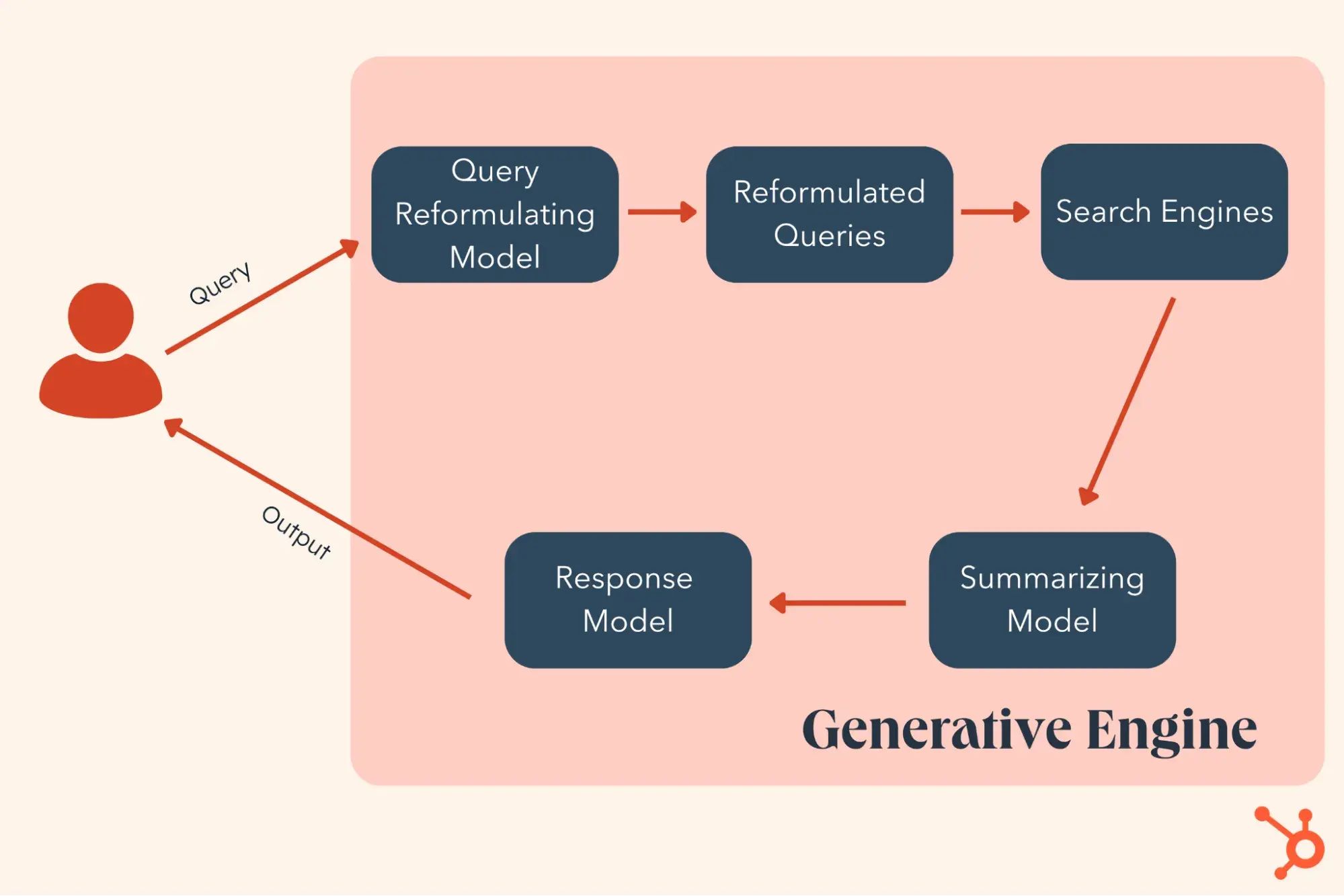
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is a new technique for maximizing your digital content’s visibility. Instead of traditional SEO practices that focus on ranking on SERPs, GEO is about being used by generative AI engines.
Generative engines pull information directly from web content to deliver responses to user queries. They use large language models (LLMs) to make sense of the info they’ve scraped and provide coherent, relevant answers.
ChatGPT, Perplexity AI, and Google AI Search are all examples of generative engines.
Generative engines work by:
- Interpreting a user’s query.
- Leveraging personal data it may have on the user, such as preferences or conversation history.
- Searching to find relevant answers to the query
- Synthesizing information from these documents into a straightforward response
GEO vs. SEO
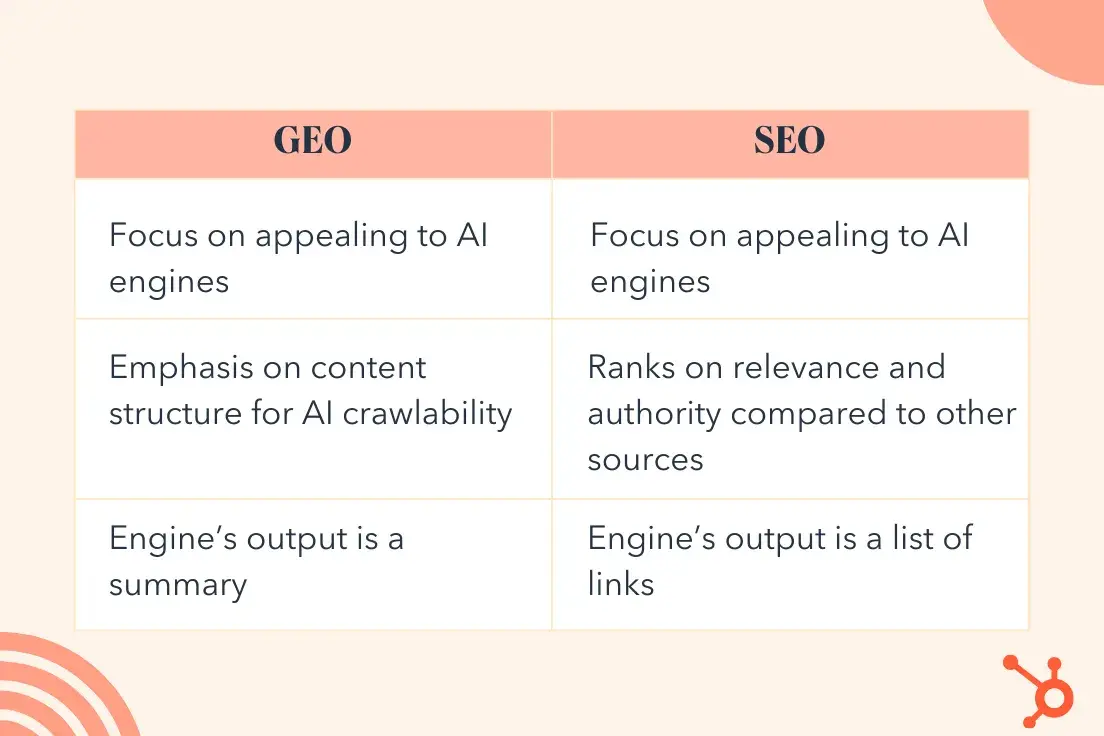
GEO and SEO are similar in many ways, as both find relevant, credible content to answer user inquiries. But they also have three key differences.
Focus
GEO focuses on making content discoverable to AI, while SEO is about improving SERP rank.
While SEO is generally related to Google and Bing, there are lots of generative engines, so it’ll be interesting to see if different engines use different qualities to determine their sources.
Emphasis
The primary techniques for SEO emphasize things like backlinks and keywords, while GEO techniques emphasize structure.
An AI bot’s job is easier when it can pull clear, concise snippets that are easily synthesized, so it makes sense why structure would be an emphasis.
Output
The key difference is the output of the engines.
GEO optimizes content for AI engines, which produce a summary as the output.
SEO, on the other hand, optimizes content for traditional search engines, which produce a ranked list of sources as the output.
How is GEO impacting SEO?
SEO experts worldwide have cited generative AI as the number one disruptor to SEO. So it’s worth understanding more about what experts suspect the impact will be.
I spoke with an expert on SEO, Nick Baird, to hear about his thoughts on GEO and how he thinks it will change SEO and digital marketing.
“First, top-of-funnel informational terms, which are the industry’s bread and butter, are going to take a huge hit. Since answers will come right in the SERP, why would people click away to websites?” Baird notes.
Secondly, Baird says, informational searches will be tough to win. However, local SEO won’t change because of generative AI.
“When people search locally, they‘re hoping to find a plumber to fix their toilet or a mechanic to fix their car. ChatGPT can’t help with that. Google will continue pointing people to local service businesses in this case,” Baird says.
His thoughts about TOFU terms are the most interesting to me. I see his point and, as a user, I’m definitely engaging less with sites when I’m looking for a short answer. I’m interested to see how high-ranking topics evolve.
How does Generative Engine Optimization work?
Learning to use GEO is simpler than it sounds and, in many ways, is overlapped with best SEO practices. AI tools respond well to clear, well-structured information that it can easily synthesize.
This means you should:
- Ensure your content is easy to read and understand.
- Incorporate credible sources, quotes, and statistics to enhance the content’s richness and authority.
- Structure your writing to align with the patterns used by generative engines.
When I’m writing an article, I focus on clear headings, concise paragraphs, lists, and well-sourced information. The same is true for best practices when it comes to SEO — so don’t worry about reinventing the wheel.
Other ways to improve GEO are using AI-friendly structured data, focusing on user intent, using easy-to-read/conversational language, and using unique words to make the content stand out.
These best practices aren’t all that different from SEO best practices. And, as with SEO, there’s no indication that AI-created content is ranking poorly.
If your content is high quality, you shouldn’t experience any sort of penalty for leveraging AI content tools, like the ones offered by HubSpot.
Image Source
Tips for Navigating the Generative SEO Landscape
Succeeding at GEO isn’t too different from traditional SEO practices. Here are a few tips to keep in mind as you start writing content for generative AI.
Cite sources and use statistics.
I also asked Baird what digital marketers who are hoping to create AI-scannable content should do, and he recommended starting with strong EEAT (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness).
These four factors are currently used by Google’s algorithm to determine how pieces rank in search.
“The more proof of a human author, rather than AI, the better. Domain authority becomes even more important as well,” Baird says.
While you can still use AI tools to write your content, it’s vital that it reads as useful, credible content. Incorporating EEAT is a great way to increase credibility, and that serves to improve your entire domain’s authority.
So what exactly does EEAT look like? I’ve been navigating the shift first hand for my HubSpot posts.
I start by looking at my own personal experience. Do I have lived experience in a subject matter? Can I include any personal anecdotes about when I’ve encountered the topic?
Beyond that, I try to showcase my authority on a subject, noting how long I’ve worked in the field.
Obviously, I am not an expert in every topic I want to cover. In that case, I do extensive research. I find original statistics with verified information. I talk to experts whose quotes I can showcase throughout my work.
These elements enhance the credibility and uniqueness of my content.
Optimize for readability.
Think of AI like a busy student frantically looking for information to use in a paper.
They don’t have time to decipher complicated sentences. They want information that’s clear and easy to understand from the get-go. Which brings me to my next tip: Use clear, concise language and scannable paragraphs.
I’ll be honest: Writing short, clear sentences may not always be my first instinct. When I’m discussing a complicated topic, my first draft often includes lengthy explanations. I then use Hemingway, an app designed to help you write clearly.
Hemingway lets me know which sentences are lengthy, confusing, or overly complicated. I can’t always get every sentence to green, but I make an effort to correct phrases marked as “very hard to read.”

Image Source
Focus on content quality.
In the past, having the right keywords was enough to win in search. Let’s take a classic example: recipe blogs.
I remember searching for a brownie recipe for a party and finding a promising, top-ranking article.
When I clicked on it, I had to scroll past huge chunks of text about what goes into a brownie, when brownies became popular, how the author’s kids loved the brownies, so on and so forth.
Why? The author knew having the word “brownie recipe” as many times as possible would help her rank.
Well, that may no longer be the case. In today’s landscape, knowing that the recipe has been passed down from older generations and won an award in a local competition would be enough to show credibility.
TL;DR: Make sure your content is relevant to potential search engines, and avoid keyword stuffing. Your audience and AI care more about the quality of your post.
Monitor trends and track your results.
Stay on top of AI engine evolution. GEO is a new technique, so expect best practices to emerge over time. Trends in the search landscape are continuously changing.
Right now, Google is prioritizing EEAT, but that may change as AI overviews take over the scene.
Keep an eye on the traffic and conversions of posts you’ve written using GEO best practices. You can also leverage HubSpot’s new AI Search Grader, which lets you know how in line your posts are with GEO.
Generative Engine Optimization FAQ
What is GEO?
Generative engine optimization (GEO) is a method of improving your content’s visibility to AI generative engines, increasing its reach.
How do I structure my content for GEO?
Ensure your content is clear, well-organized, and has credible sources. Take advantage of lists and H2s and incorporate quotes and statistics when possible.
How do I check if my content is optimized for GEO?
Because GEO is so new, there aren’t many tools to measure how successful your content will be with AI generative engines. HubSpot’s AI Search Grader App is the only tool on the market that can scan your content for its GEO performance.
All you have to do is drop your URL into the grader. From there, you’ll have custom suggestions on what areas you can change to optimize your AI search performance.
That may include including more authority and personal experience or shifting the focus area of your page.
What is AI looking for in GEO content?
Large language models (LLMs) are looking for clear, well-structured information that they can pull and summarize to respond to user queries.
AI scanning works best for content that:
- Uses headers and lists
- Incorporates expert quotes
- Cites sources
- Uses simple language and scannable paragraphs
Is GEO going to replace SEO?
No — search engines aren’t going anywhere, so SEO isn’t, either. It’s best to consider GEO as an extension of SEO practices, as opposed to a replacement.
Best practices (like using H2s and credible citations) are shared between GEO and SEO, as are worst practices. Keyword stuffing, for example, has a negative impact on both SEO and GEO.
How can you measure GEO success?
Liam Carnahan, an SEO coach and content strategist, has a recommendation for how you can leverage existing tools to check if your article is getting picked up by AI engines.
“Of all the popular search-oriented options out there right now, Perplexity does the best job of citation,” Carnahan says.
He continues, “So when I‘m trying to understand whether LLMs are ‘enjoying’ my content, I’ll go there first, and type in questions and prompts I imagine people might ask, using keywords I know my content is ranking for, to see how often it shows up in citations there.”
Carnahan also notes that this isn‘t the most elegant solution, but “for now, it can give me a good idea about which of my clients’ content is ranking in AI results, and which content pieces are missing the mark.”
What’s Next for GEO
My biggest takeaway from exploring GEO is that it emphasizes different things, but in many ways, is similar to SEO. While SEO focuses on keyword optimization and backlinks, GEO focuses more on content structure.
Content writers are going to have to balance both but, thankfully, they click together well. I think we’re going to see clearer, more helpful content as a result of these two strategies — which is something I’m really excited about.
AI isn’t going anywhere. While we’re still learning how to use and measure GEO, it’s clear that keeping an eye on emerging techniques is going to be the key to success in the digital content world going forward.
Credit: Source link